Osteochondrosis is a degenerative process that occurs in articular cartilage and adjacent bone tissue.Doctors define this disease as a degenerative-destructive lesion of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs: they lose moisture, decrease in height and elasticity.
Osteochondrosis “looked younger”
If just a few decades ago, articular cartilage began to deteriorate in people over the age of 40, today the disease occurs even in adolescence.
Doctors cite many reasons to explain this unpleasant trend.An unhealthy lifestyle, combined with an unfavorable environmental situation and a deterioration in the standard of living, causes premature wear and deformation of bone and cartilage structures.
Constantly being in an unnatural position, a sedentary lifestyle and poor diet accompany every person.Few people think about the prevention of osteochondrosis, neglecting physical exercise, a balanced diet and an approach aimed at maintaining their own health in general.The result of such thoughtlessness is usually sad.
Main causes of osteochondrosis
Experts still argue about how many real factors contribute to the formation of the disease.Unconditional reasons include:
- individual predisposition;
- segmental circulatory disorders;
- changes acquired with age;
- damage to the annulus fibrosus;
- overweight;
- constant loads;
- poor diet;
- bad habits;
- failure of the body during menopause;
- sedentary work.
Stages of development of osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is classified by stages, taking into account clinical signs, the degree of tissue damage and the patient's level of discomfort.The pathological process occurs in four stages:
- Preclinical.First, the basic level of nutrition of the intervertebral discs decreases, their elasticity and firmness deteriorate.No changes can be detected on X-ray. The patient may experience slight fatigue, slight discomfort, stiffness, dizziness, headache;
- Stage of discogenic radiculitis.The annulus fibrosus begins to slowly deform (cracks and protrusions appear).The pain becomes more severe and sudden, the discomfort becomes more noticeable.A symptom such as "lumbago" appears, the limbs begin to go numb;
- Vascular-radicular stage.The fibrinous ring completely loses its shape.From this point on, hernias can form.X-rays are very informative.Subjective sensations of patients are pronounced (pain, acute pain attacks, constant discomfort).Frequent muscle spasms appear and performance decreases sharply.If nerve fibers suffer, the first signs of dysfunction of internal systems are inevitable;
- As the height of the vertebrae decreases, friction between them begins.Osteophytes may appear as a compensatory mechanism.These are specific osteogrowths which help to strengthen the area where the friction was the most intense.But osteophytes can cause inflammatory processes in the surrounding soft tissues, thereby aggravating the pathological picture.
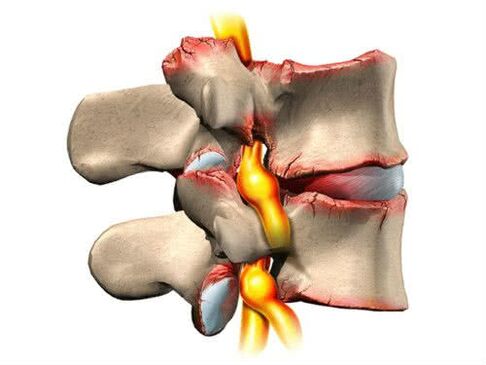
Disease symptoms: focus on patient well-being
Osteochondrosis is characterized by a whole galaxy of very different symptoms.This is due to the vastness of the pathological process itself and its influence on most organs of the human body.There are several main syndromes that manifest in patients suffering from osteochondrosis:
- Static syndrome.When the vertebrae lose their shape, your posture inevitably changes.Signs of kyphosis, scoliosis and lordosis appear.The discomfort is accompanied by a feeling of stiffness;
- Neurological syndrome.Damage to nervous tissue leads to paresthesias (impaired sensitivity) of different areas, accompanied by a feeling of numbness, tingling, “crawling”;
- Vascular syndrome.Due to compression (squeezing) of large vessels and capillaries by deformed vertebrae, blood circulation is disrupted.Result: nausea, dizziness, pallor, signs of lack of oxygen;
- Symptom of trophism.Since tissue nutrition is disrupted (due to compression of small vessels), trophic ulcers may appear on the surface of the skin.
Cervical osteochondrosis
The first manifestation of cervical osteochondrosis is a headache.Painkillers do not relieve pain.As a rule, the pain begins in the parietal area and gently flows to the temporal region.Over time, the patient begins to experience discomfort and numbness in the shoulder girdle.
Due to impaired blood supply to the brain, a person may experience dizziness, nausea, and increased tinnitus.If the nutrition of the optical zone is disturbed, visual acuity usually decreases sharply.
Older people may suddenly lose consciousness and have difficulty with memory and coordination.Rare symptoms include shortness of breath, anxiety and hiccups.
Thoracic osteochondrosis
The thoracic region is the least frequently affected.One of the main reasons for the occurrence of pathology is considered to be scoliosis and inappropriate work in the office (that is, sedentary work).The patient feels dull, aching pain from the beginning of the development of the disease.As the disease progresses, it causes other symptoms: chest pain, numbness, paresthesias, aching pain in the liver and kidneys.
In the differential diagnosis, deformation processes in the thoracic region can be confused with myocardial infarction and intercostal neuralgia.This ECG and a more in-depth examination (absence of cyanosis, pallor, yellowness of the skin) help clarify the diagnosis.
Lumbosacral osteochondrosis
The most common type of osteochondrosis.This is because this area of the spine bears the greatest load.Hernias most often occur here, complicating the clinical picture.
The main symptoms: prolonged pain, sensations of sore muscles, discomfort, rare lumbago, paresthesias which stop from time to time and then resume.The degree of sensitivity of the skin of the feet, legs and thighs may change.
A common cause of osteochondrosis in this department is trauma, mechanical compression and intense physical activity.One of the most unpleasant consequences of lumbosacral deformities is the “slippage” of the vertebra and problems in the functioning of neighboring organs.
What osteochondrosis pain will tell you about
Depending on where the deformation processes occur most intensely, the nature and specificity of the pain depends.The main characteristic: damaged vertebrae pinch the nerve roots, causing pain in the area for which the nerve plexuses are responsible.
The problems can be divided as follows:
- Cervical region – headaches, stiffness of the neck and shoulders, disturbances in vision, breathing and other important functions;
- Thoracic region - pain in the heart, lumbago in the arm and internal organs, impaired digestive function, arrhythmias, problems in the functioning of the endocrine system.The pain is always strong and sharp;
- Lower back – aching and constant pain, dysfunction of the genitourinary system, pelvic congestion, reproductive dysfunction.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
The doctor must take as complete anamnesis as possible.During the examination, the specialist palpates the areas where the pain is most pronounced.
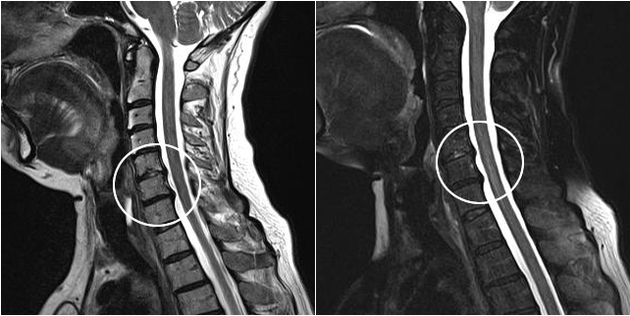
An x-ray examination will be informative.Especially in the later stages of the disease.
Modern diagnostic methods include MRI and CT scanning, which make it possible to most accurately examine the processes of destruction of cartilage and bone tissue.In addition, thanks to this technique, it is convenient to diagnose hernias and other soft tissue defects near the source of the disease.
For the differential diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, an ECG is used.The patient must undergo a general blood and urine test.
Working on a computer and the development of osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is an insidious disease.This affects both the “office plankton” who sit at the computer all the time and the hard-core workers who put their health under extraordinary stress.Irrational work, non-compliance with the rules for preventing osteochondrosis and an unhealthy lifestyle cause the rapid destruction of bone and cartilage tissue.
The modern youth generation is too “computerized”.Many health professionals cite this as one of the main reasons why osteochondrosis has become so common and affects very young people.Top Expert Tips:
- It is necessary to monitor your posture and position at your desk;
- Even during hard work, it is important to take a break and “stretch” the body;
- You cannot tolerate discomfort when sitting at the computer.The body, especially the back, should be comfortable;
- Active lifestyle.Work or leisure in front of the computer should alternate with sports leisure or light gymnastics.
Bad lifestyle
An unbalanced diet causes osteochondrosis.Junk food attacks on several “fronts” at once.First of all, obesity caused by fast food and similar snacks is one of the underlying causes of spinal dysfunction.And the deposited salts and other harmful elements in the bones only aggravate the problem, accelerating the destructive processes.
Alcohol and tobacco have similar effects.Harmful substances affect the cellular level, having a destructive effect on the surfaces of bone tissue and cartilage, which are most sensitive to nicotine.
By revising your lifestyle, diet and eradicating bad habits, you can prevent the appearance or progression of osteochondrosis.The ability to move easily and freely is a true luxury, a gift of nature for everyone.Unfortunately, the value of painless movement only becomes apparent when the disease process immobilizes the human body.
Taking care of your health today means a happy and fulfilling life in the future.
















